Vitamin B12, or Cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin that your body needs to stay healthy. Since the body can’t make it on its own, we must get it through food or supplements.
It plays a key role in forming red blood cells, supporting brain and nerve function, and converting food into energy. Without enough B12, people may feel tired, weak, or mentally foggy. It also helps maintain the protective layer around nerves, ensuring signals travel smoothly between the brain and the body.
There are three main forms of Vitamin B12, each with specific uses:
- Methylcobalamin – A natural, active form commonly used in supplements. It supports the nervous system and is easily absorbed by the body.
- Mecobalamin – A clinical version of methylcobalamin, often found in tablets and injections prescribed in India. It’s widely used for nerve-related issues, especially in diabetic patients.
- Cyanocobalamin – A synthetic form used in many fortified foods and basic supplements. The body converts it into an active form after intake.
Each type has its place depending on the person’s health and how well their body absorbs nutrients. Doctors often recommend the right form based on symptoms, severity, and lifestyle.
In short, B12 helps your body produce energy, think clearly, and keep nerves and blood healthy — making it essential at every stage of life.
Powerful Health Benefits of Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 does far more than people often realize. While it’s known for boosting energy, its benefits extend across nearly every system in the body — from the brain and nerves to the skin and digestive health.
One of the most noticeable effects of B12 is how it helps reduce tiredness and fatigue. It plays a direct role in converting food into usable energy, which is why many people with low B12 levels feel constantly drained, even with enough sleep. Along with better energy, B12 also supports memory and mental clarity. It’s involved in producing neurotransmitters — the brain’s chemical messengers — and helps maintain focus, concentration, and a balanced mood.
Vitamin B12 also keeps red blood cell production steady, which is crucial for carrying oxygen throughout the body. A deficiency here can lead to anemia, which often causes pale skin, shortness of breath, and weakness. In pregnant women, adequate B12 helps reduce the risk of birth defects by supporting proper brain and spinal development in the growing baby.
Another area B12 supports is bone health. Research has linked low B12 levels with decreased bone density, especially in older adults. Similarly, people with consistent fatigue or mild depression may sometimes be lacking B12, as it’s essential for mood balance and nervous system function.
Beyond the internal organs, B12 plays a silent role in how we look. Healthy levels help maintain stronger hair, clearer skin, and better nail growth — mostly due to its effect on cellular regeneration and oxygen flow. It also aids digestion by keeping the gut lining healthy and indirectly improving the absorption of nutrients.
Lastly, B12 supports immune defense by keeping nerve and blood systems strong. When these are working well, the body is better equipped to respond to infections and everyday stress.
Even though B12 is just one vitamin, its impact is wide and foundational. A deficiency might not be obvious at first, but over time, it can affect everything from energy to emotional health. That’s why consistent intake through food or supplements can make a real difference in overall well-being.
Signs of Vitamin B12 Deficiency You Shouldn’t Ignore
Vitamin B12 deficiency often develops slowly and silently, but its effects can be deeply disruptive if left untreated. Early symptoms may feel general — like tiredness or forgetfulness — but over time, they can impact nerve health, mood, and memory.
Common signs to watch for:
- Fatigue that doesn’t improve even after rest or sleep
- Brain fog, difficulty concentrating, or forgetfulness
- Numbness or tingling in hands and feet
- Poor balance or unsteady walking
- Pale skin and shortness of breath
These symptoms appear because B12 is responsible for producing healthy red blood cells and protecting the nervous system. When levels drop too low, oxygen delivery slows down and nerves begin to weaken.
Long-term risks if left untreated:
- Permanent nerve damage due to loss of the protective coating around nerves
- Memory loss or cognitive decline
- Mood disorders, including depression or irritability
- Reduced mobility or coordination in older adults
Some people are more likely to develop B12 deficiency than others, often due to diet or medical conditions.
People at higher risk include:
- Vegetarians and vegans – since B12 is mostly found in animal-based foods
- Elderly individuals – absorption decreases with age
- Pregnant women – due to higher nutritional demands
- People on diabetes medication – especially long-term metformin users
Identifying the signs early and understanding your risk can help avoid serious health issues. With the right supplements or dietary changes, most people can correct B12 deficiency before it causes lasting harm.
Mecobalamin vs Methylcobalamin: What’s the Real Difference?
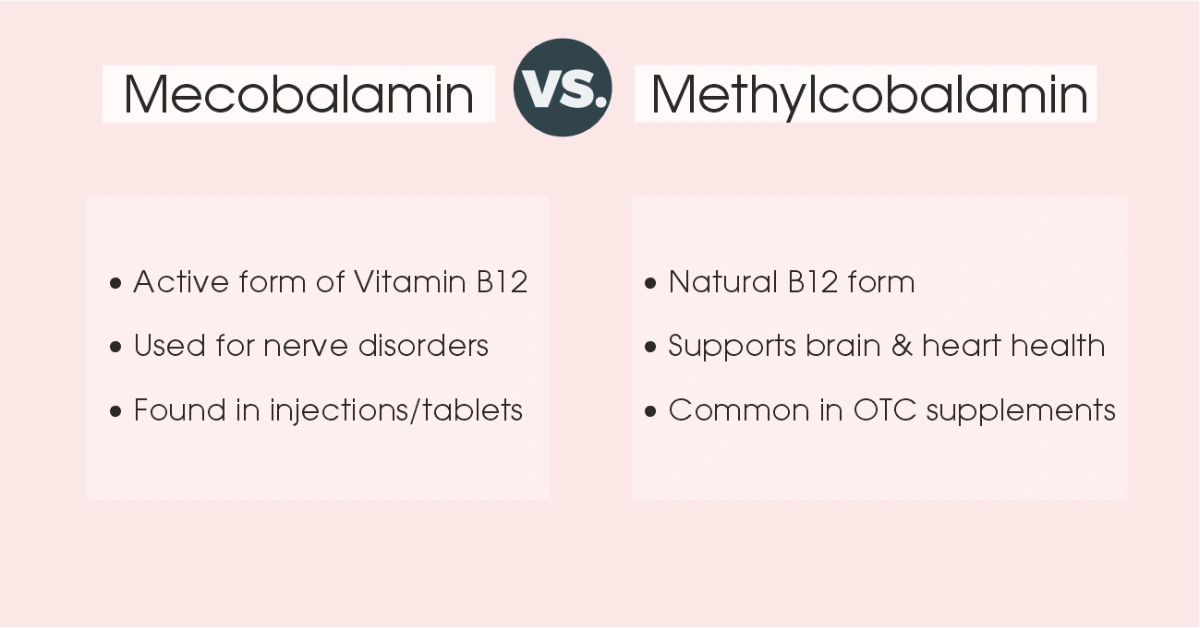
Both Mecobalamin and Methylcobalamin are active forms of Vitamin B12, meaning your body can use them directly. But they’re not exactly the same. While they share the same core purpose — restoring B12 levels — their usage, availability, and medical role differ in subtle but important ways.
Methylcobalamin is the form found naturally in foods like eggs, dairy, and meat. It’s commonly used in dietary supplements, especially in over-the-counter B-complex capsules. On the other hand, Mecobalamin is a purified, pharmaceutical-grade version of Methylcobalamin. It’s widely used in India for treating nerve-related disorders, especially when nerve damage or degeneration is involved.
Here’s how the two compare:
| Feature | Methylcobalamin | Mecobalamin |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural, found in food | Lab-purified form for clinical use |
| Usage | General supplementation | Nerve regeneration, neuropathy cases |
| Availability | Mostly in OTC supplements | Common in prescribed tablets/injections |
| Absorption | Well-absorbed orally | Also available in injectable forms |
| India preference | Used in multivitamin combos | Preferred for diabetic nerve care |
| Dosage range | 500–1500 mcg (oral) | 500–1500 mcg (oral/injection) |
Doctors often choose mecobalamin when there’s a clinical need for nerve repair — like in cases of diabetic neuropathy, sciatica, or long-term B12 deficiency. It’s especially effective in restoring the myelin sheath that protects nerve fibers.
For example, Rolam-Plus includes Mecobalamin with Alpha Lipoic Acid and B vitamins, making it suitable for patients with both nerve and energy issues. RegiJoint Pro uses Mecobalamin along with collagen and joint-support nutrients to support both flexibility and nerve strength — useful in elderly or post-surgery recovery.
So while both forms deliver Vitamin B12, Mecobalamin’s role in pharma is more targeted and therapeutic, especially for people dealing with nerve health concerns.
Vitamin B12 Injections, Capsules & Tablets: Full Comparison
Not all Vitamin B12 supplements work the same way — and not everyone needs the same form. While many people rely on capsules or tablets for regular use, there are times when injections or even syrups are a better choice.
B12 injections are usually recommended when there’s a severe deficiency or when the body can’t absorb B12 well through the digestive system. This is common in conditions like pernicious anemia, long-term use of antacids or metformin, or after gastrointestinal surgeries. In such cases, injections help deliver the vitamin directly into the bloodstream, bypassing the gut entirely.
For general maintenance or mild deficiency, oral tablets and capsules are usually enough. They’re easy to take, affordable, and effective for most people with functioning digestion. Supplements like Rolam-Plus or Zefol Cap offer convenient daily doses in combination with other helpful nutrients like iron, folic acid, and zinc — especially helpful in fatigue, low immunity, or during recovery.
Here’s a simple comparison to understand their differences:
| Form | Best For | Speed of Action | Convenience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Injection | Severe deficiency, poor absorption | Fastest (direct) | Requires clinic or self-injection |
| Tablet/Cap | General use, daily support | Moderate | Very easy to use |
| Syrup | Children, elderly, digestive issues | Moderate | Gentle & flexible |
Injections are often given weekly or monthly depending on the deficiency level. Tablets like Rolam-Plus (mecobalamin + B-complex) or Zefol (B12 + iron + folic acid) are suitable for long-term oral support and are widely available in India without needing complex administration.
What About Syrups & Suspensions?
Some people — especially children, elderly patients, or those with digestive issues — may find it hard to swallow pills or properly absorb them. In such cases, B12 syrups or suspensions offer a gentle yet effective alternative.
Products like Becly Syrup (containing B1, B6, B12, Lysine) and Zest-SF (with B12, iron, folic acid, zinc) combine essential nutrients in liquid form. These are not only easier to consume but may also help with improved compliance in patients recovering from illness or facing chronic fatigue.
While the form may change, the goal stays the same — making sure your body gets enough Vitamin B12 to stay sharp, strong, and energized.
How to Get Tested for Vitamin B12 Deficiency
If you’re often feeling low on energy, struggling to focus, or noticing tingling in your hands or feet, it might be time to test your Vitamin B12 levels. Many people live with a deficiency for months or even years without realizing it, simply assuming they’re just tired or overworked. But a simple test can give you a clear answer.
Who should consider testing?
Testing isn’t just for people with visible symptoms. Some individuals are more likely to develop B12 deficiency due to age, medical conditions, or lifestyle. You should consider getting tested if you:
- Follow a vegetarian or vegan diet
- Are over the age of 50, when nutrient absorption often declines
- Are pregnant or planning pregnancy
- Have a condition like diabetes, gastritis, or celiac disease
- Are taking metformin, antacids, or similar long-term medications
- Feel unexplained fatigue, dizziness, memory loss, or numbness
What’s the testing process?
The most common test is a serum Vitamin B12 blood test. It’s a quick and routine procedure where a small blood sample is drawn, usually from the arm, and sent to the lab for analysis. In most cases, fasting is not required, but your doctor may advise it if additional tests are being done alongside.
Cost of Vitamin B12 test in India
The average price of a Vitamin B12 test in India typically ranges from ₹400 to ₹800, depending on the lab, location, and whether it’s part of a larger health package. Many diagnostic centers also offer combo tests that include folic acid, iron, and B12 in one profile — ideal for people facing long-term fatigue or weakness.
Getting tested early can help catch a deficiency before it turns into a bigger health issue. With just one simple test, you can take the first step toward restoring your energy, focus, and overall health.
Top Natural & Medical Sources of Vitamin B12

Vitamin B12 is one of those nutrients that your body truly depends on — but can’t make on its own. That’s why it’s important to understand where it comes from, both naturally through diet and medically through supplements.
Natural sources from food
B12 is mainly found in animal-based foods, which is why vegetarians and vegans often struggle to maintain adequate levels. If you’re looking to increase your intake through diet, these foods are the most reliable:
- Fish – especially salmon, tuna, and sardines
- Red meat – like beef and lamb
- Poultry – including chicken and turkey
- Eggs – particularly the yolk
- Dairy products – such as milk, cheese, and yogurt
These sources not only provide B12 but also offer other nutrients like protein, iron, and healthy fats that support overall wellness.
For those who avoid animal products, some plant-based items can help — but only if they’re fortified during processing. Examples include:
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Plant-based milk alternatives (like soy or almond milk with added B12)
- Nutritional yeast, which is popular in vegan cooking for its cheesy flavor and added B12 content
While these options can help reduce the risk of deficiency, they may not be enough for people with higher needs or absorption issues.
Medical sources: when food isn’t enough
Sometimes, diet alone isn’t sufficient. This is where medical sources of B12 come in — especially for individuals with digestive disorders, older adults, or those recovering from illness.
The three most common forms include:
- Injections – Fast-acting, used in moderate to severe deficiencies
- Capsules or tablets – Daily use, often combined with iron, folic acid, or B-complex
- Syrups and suspensions – Ideal for children, elderly, or those with swallowing difficulties
Products like Rolam-Plus, Zefol, Becly Syrup, and Zest-SF Suspension are all examples of how B12 is medically delivered for different needs — whether it’s nerve support, fatigue management, or post-illness recovery.
Knowing your options helps you make the right choice — through diet, supplements, or both — to keep your B12 levels right where they need to be.
Why Vitamin B12 Is a Must-Have in Modern Pharma Products
In today’s pharmaceutical landscape, Vitamin B12 is no longer seen as just a basic supplement — it’s a core ingredient across multiple therapeutic segments. Whether it’s managing fatigue, treating nerve damage, or supporting recovery in chronic illness, B12 has earned its place in both preventive and curative medicine.
Its role in nerve protection is one of the main reasons it’s included in neuro-support capsules and injections. Mecobalamin, a pharmaceutical-grade form of B12, helps in regenerating nerve fibers and improving signal transmission — making it a preferred choice in diabetic neuropathy, sciatica, and even post-viral nerve weakness.
But its applications go beyond neurology. In pregnancy supplements, B12 is combined with folic acid and iron to support fetal brain development and prevent neural tube defects. It’s also used in immunity-boosting tonics, where it helps maintain white blood cell function and reduces fatigue in recovering patients.
In cases of anemia or chronic fatigue, B12 improves red blood cell formation, especially when paired with iron and folic acid. Products like Zefol Cap combine all three to address nutritional anemia in a simple daily dose. Similarly, Rolam-Plus Cap delivers nerve support by combining mecobalamin with Alpha Lipoic Acid and B-complex vitamins — useful in post-diabetic care or general weakness.
Even joint-care combinations now include B12, not just for reducing stiffness, but to support nerve-muscle coordination. RegiJoint Pro, for example, brings together collagen, minerals, and mecobalamin to help aging adults maintain mobility.
For pediatric or geriatric use, liquid formats are often preferred. Becly Syrup and Zest-SF Suspension are both rich in B12, folic acid, and other vital nutrients — helping with appetite, growth, and energy in weaker or recovering patients.
Across capsules, syrups, or injections, B12 proves its value time and again — not as a standalone solution, but as a powerful part of modern formulations that aim to heal, protect, and strengthen.
Vitamin B12 in the PCD Pharma & Third-Party Market
Vitamin B12 continues to be one of the most in-demand ingredients in the Indian pharma space, especially among general practitioners who see a steady flow of patients with fatigue, weakness, nerve complaints, and nutritional deficiencies. For PCD pharma companies and third-party manufacturers, this isn’t just a trend — it’s a long-term opportunity backed by real prescription behavior.
Doctors regularly recommend B12 combinations for a variety of conditions — from diabetic neuropathy and chronic anemia to recovery after illness or surgery. These prescriptions are not limited to specialists. GPs, gynecologists, pediatricians, orthopedics, and neurologists all include B12-based products in their daily practice. This wide base makes B12 combos a reliable category for sustained product movement.
Top-selling products often combine mecobalamin or methylcobalamin with ingredients like Alpha Lipoic Acid, Vitamin D3, Zinc, Iron, and Folic Acid. These combinations offer multi-action support — nerve care, blood health, immunity, and energy — which explains their continued success across cities and towns.
For PCD pharma franchise owners, this is a powerful range to build on. Offering capsules like Rolam-Plus, suspensions like Zest-SF, and B-complex syrups like Becly allows coverage across adult, pediatric, and elderly patients. These are not niche products — they’re staples in every district’s prescription cycle.
Third-party manufacturers also benefit from the stable demand and fast turnaround of B12 products. With formulations that are already approved and DCGI-compliant, production timelines are shorter, and customization is easier based on brand preferences or regional targets.
In short, adding or expanding your B12 product line isn’t just smart — it’s strategically necessary in today’s market. Whether it’s to strengthen your neuro range, diversify your general health offerings, or tap into B-complex demand, Vitamin B12 is a must-have in every modern pharma portfolio.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Underestimate This Micro Powerhouse
Vitamin B12 isn’t just another supplement on the shelf — it’s a core building block that quietly supports everything from mental clarity to physical strength. At every life stage, it plays a different but essential role. In children, it fuels growth and cognitive development. In adults, it keeps energy levels stable, nerves responsive, and memory sharp. And as we age, it helps preserve mobility, mood balance, and immunity.
That’s why the form you choose matters. For those with severe deficiencies or absorption issues, injections offer the fastest recovery. If you’re looking for long-term support, capsules or tablets like Rolam-Plus or Zefol are convenient and effective. And for kids, elderly, or anyone with swallowing difficulty, syrups and suspensions like Becly or Zest-SF make daily dosing simple and stress-free.
But knowing isn’t enough — being proactive is key. Whether it’s checking in with a blood test, spotting early signs of deficiency, or picking the right supplement for your needs, small steps can prevent bigger health issues later.
Vitamin B12 may be microscopic in size, but the difference it makes in how you feel, think, and function is anything but small.
What is the ideal daily dose of Vitamin B12?
500–1500 mcg per day is common for adults, depending on need and absorption.
Is Vitamin B12 safe for daily use?
Yes, it’s water-soluble and safe to take daily in recommended amounts.
What is the best form: methylcobalamin or mecobalamin?
Methylcobalamin suits general use; mecobalamin is preferred for nerve issues.
What are the symptoms of B12 deficiency?
Fatigue, numbness, brain fog, poor balance, and mood changes.
Can B12 improve energy and brain function?
Yes, it boosts energy levels and supports memory and focus.



